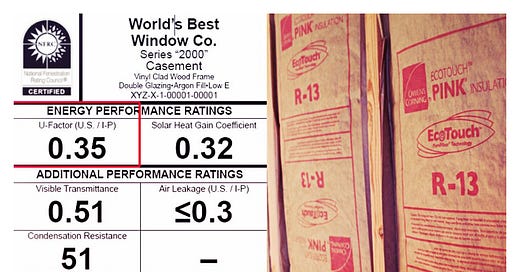
Window efficiency is measured with U-values unlike insulation which is measured in R-val
ues. Why couldn’t they make it easier and use the same values? It’s not that simple.
Both R-values and U-values are two different measures of how well materials perform to keep your building comfortable in different seasons. The R-value measures a material’s resistance to the flow of heat, and the U-value measures the conductance of heat based on temperature and thickness of the unit.
R-Value is often used for insulation (higher is better)
R-values help people understand how different materials transfer heat so that you can choose building materials that keep the heat inside during winter and outside in the summer.
Heat always moves from the hotter object to the colder one. So a heated house in winter is always losing heat to the colder air outside. When you install insulation, it slows the passage of heat. The higher the R-value, the more effective the material is at reducing heat transfer. For example, a fleece jacket or wool sweater provides better insulation than a cotton sweatshirt, meaning they keep you warmer. Fleece and wool resist the flow of heat better than cotton and therefore have higher thermal resistance which is represented by R-value.